The threat of substitute products:
The existence of products outside of the realm of the common product competitors which increases the propensity of customers to switch to alternatives
- buyer propensity to substitute
- relative price performance of substitutes
- buyer switching costs
- perceived level of product differentiation
In relation to Hollister Co. their main competitor would be Abercrombie & Fitch. In relation to having the advantage over Abercrombie & Fitch it would be the price of the merchandise. Although Abercrombie & Fitch are a bigger name, many people choose to opt for Hollister Co. and its clothing is the same but the price is a lot cheaper, the use of having Mid-Season, and Christmas sales every so often attracts people to be shopping at Hollister Co.
The threat of the entry of new competitors:
Profitable markets that yield high returns will draw firms. This results in many new entrants, which will effectively decrease profitability. Unless the entry of new firms can be blocked by incumbents, the profit rate will fall towards a competitive level (perfect competition).
- the existence of barriers to entry (patents, rights, etc.)
- economies of product differences
- brand equity
- switching costs or sunk costs
- capital requirements
- access to distribution
- absolute cost advantages
- learning curve advantages
- expected retaliation by incumbents
- government policies
In relation to Hollister Co. if a new company came about their would be a chance of decrease profitability. Hollister Co. have a specific target market, there clothes are designed for “young, cool and neat” people. There competitors Abercrombie & Fitch are expensive and Hollister Co. is a lot cheaper this gives them the edge, most of their customers wouldnt be buying for example, a so called expensive tee-shirt and then a cheap pair of jeans from Primark, they will be buying full outfits or equally buying high brand names, as a globally recognised company that are already out in the market, they would already have the edge over any new competitor because of their high profile status.
The intensity of competitive rivalry:
For most industries, this is the major determinant of the competitiveness of the industry. Sometimes rivals compete aggressively and sometimes rivals compete in non-price dimensions such as innovation, marketing, etc.
- number of competitors
- rate of industry growth
- intermittent industry overcapacity
- exit barriers
- diversity of competitors
- informational complexity and asymmetry
- fixed cost allocation per value added
- level of advertising expense
- Economies of scale
- Sustainable competitive advantage through improvisation
In relation to Hollister Co. and it competitor Abercrombie & Fitch, for example if Hollister Co. see an oppurtunity after christmas when most people don’t have money and class=”hiddenGrammarError” pre=”and “>there income would be as much they may have a sale by reducing sale items by 25%, and Abercrombie & Fitch may respond by making their sale 30% off. The rivalry can be a good thing though, it can bring out the best in the company and exploit new strategies and techniques and have the edge over its customer.
The bargaining power of customers:
Also described as the market of outputs. The ability of customers to put the firm under pressure and it also affects the customer’s sensitivity to price changes.
- buyer concentration to firm concentration ratio
- degree of dependency upon existing channels of distribution
- bargaining leverage, particularly in industries with high fixed costs
- buyer volume
- buyer switching costs relative to firm switching costs
- buyer information availability
- ability to backward integrate
- availability of existing substitute products
- buyer price sensitivity
- differential advantage (uniqueness) of industry products
- RFM Analysis
As a retailing store there is no bargaining power of customers, a customer cant walk into the shop and buy 20 white tee shirts and ask for discount, there is only a discounted rate for staff. That is the reason of sales, when these items arent getting sold during a particular time, like after christmas, they’ll sell them on for a discounted rate.
The bargaining power of suppliers:
Also described as market of inputs. Suppliers of raw materials, components, labor, and services (such as expertise) to the firm can be a source of power over the firm. Suppliers may refuse to work with the firm, or e.g. charge excessively high prices for unique resources.
- supplier switching costs relative to firm switching costs
- degree of differentiation of inputs
- presence of substitute inputs
- supplier concentration to firm concentration ratio
- employee solidarity (e.g. labor unions)
Depending on the quality of the goods supplied by the supplier, they will determine the bargaining power, for example if a supplier is supplying higher quality goods than most other suppliers this can give them an incentive to ask for more money. The fact that companies such as Hollister Co. like to form a good relation with their suppliers as they can depend on them means to switch suppliers would be taken a great risk, this could result in profit lose and maybe even effect customer loyalty.
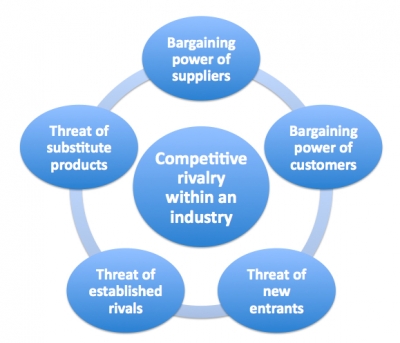
This is a Porters Five Image
Criticisms of the 5 Force model
Porter’s framework has been challenged by other academics and strategists such as Stewart Neill, also the likes of Kevin P. Coyne and Somu Subramaniam have stated that three dubious assumptions underlie the five forces:
- That buyers, competitors, and suppliers are unrelated and do not interact and collude.
- That the source of value is structural advantage (creating barriers to entry).
- That uncertainty is low, allowing participants in a market to plan for and respond to competitive behavior.
An important extension to Porter was found in the work of Brandenburger and Nalebuff in the mid-1990s. Using game theory, they added the concept of complementors (also called “the 6th force”), helping to explain the reasoning behind strategic alliances. The idea that complementors are the sixth force has often been credited to Andrew Grove, former CEO of Intel Corporation. According to most references, the sixth force is government or the public. Martyn Richard Jones, whilst consulting at Groupe Bull, developed an augmented 5 forces model in Scotland in 1993, it is based on Porter’s model, and includes Government (national and regional) as well as Pressure Groups as the notional 6th force. This model was the result of work carried out as part of Group Bull’s Knowledge Asset Management Organisation initiative.
It is also perhaps not feasible to evaluate the attractiveness of an industry independent of the resources a firm brings to that industry. It is thus argued that this theory be coupled with the Resource-Based View (RBV) in order for the firm to develop a much more sound strategy.
